Sep.
04, 2025
Contents
Comparing EDM and Laser Cutting for Modern Manufacturing Needs

When you look at EDM vs. Laser Cutting, you see that each has its advantages. The best choice depends on the specific needs of your project. EDM is known for its precision, making it ideal for cutting thick and hard materials. On the other hand, laser cutting is faster and works best with thin materials. Many companies face challenges related to cost, speed, and material compatibility. The table below illustrates how EDM vs. Laser Cutting differ in addressing these challenges:
Challenge | EDM Cutting | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|
Cost | Usually costs more because of the machines | Costs less, making it suitable for producing many parts |
Precision | Very good for tiny, exact cuts | Good, but not as precise as EDM |
Speed | Slower than laser cutting | Faster, excellent for thin materials |
Material Compatibility | Best for hard materials like steel | Compatible with a variety of materials |
Environmental Impact | Generates waste that needs to be disposed of | Cleaner process, producing less waste |
Choosing the right method between EDM vs. Laser Cutting can help you overcome these challenges and achieve your manufacturing goals.
Electrical Discharge Machining, or EDM, is used for very precise cuts. It works best on hard metals that can conduct electricity. EDM uses electrical sparks to cut the metal. The sparks come from a wire or electrode. These sparks slowly wear away the metal. This lets you make detailed shapes and designs. EDM can be very accurate, down to about ±0.001mm. It works well with metals like steel, titanium, and aluminum. New EDM machines use CNC programming and AI. This makes the process faster and easier. Touchscreens help you control the machine. Better electrode materials, like tungsten copper, give smoother finishes.
Tip: EDM is great for making molds, dies, and tools. It is often used in aerospace and medical device industries.
Process Type | Mechanism Description | Material Compatibility | Precision Range | Surface Roughness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
EDM | Uses electrical discharges to erode material | Conductive metals (steel, titanium, aluminum) | ±0.001mm to ±0.005mm | Ra 0.4μm |
Laser cutting uses a strong beam of light to cut things. It can cut many materials, not just metals. Laser cutting works on plastics, wood, ceramics, and composites. The laser moves quickly and makes smooth edges. It can cut very small shapes, as tiny as 50μm wide. This means it is very precise. New laser machines use automation and AI. They can change settings by themselves. This saves energy and helps avoid mistakes. Laser cutting is good for making patterns, prototypes, and decorations.
Process Type | Mechanism Description | Material Compatibility | Precision Range | Surface Roughness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Laser Cutting | Employs a focused laser beam to melt or vaporize material | Various materials | High precision (focus diameter within 50μm) | Smooth cutting edges |
EDM and Laser Cutting work in different ways. Each has its own strengths.
Precision: EDM is the most accurate, down to ±0.0001 inches. Laser cutting is also precise, but not as much as EDM.
Speed: Laser cutting is much faster, especially on thin materials. EDM is slower, especially with thick or tricky parts.
Material Compatibility: EDM only works on metals that conduct electricity. Laser cutting works on many things, like metals, plastics, wood, and more.
Typical Use Cases:
EDM: You use EDM for detailed designs, molds, dies, and tools. It is common in aerospace, electronics, jewelry, and cars.
Laser Cutting: Laser cutting is used for patterns on wood, acrylic, and metal. It is also used for prototypes and engravings.
Feature | Wire EDM | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|
Precision | ±0.0001 inches (±0.0025 mm) | ±0.002 inches (±0.05 mm) |
Speed | Slower, especially on thick materials | Faster, especially with thin materials |
Material Compatibility | Only electrically conductive materials | Wide range including metals, plastics, wood, ceramics, and composites |
Note: Automation and AI have made both EDM and laser cutting better. Now you can set up faster, get better quality, and save money.
Pick EDM or Laser Cutting based on what you need. If you want the best accuracy for hard metals, choose EDM. If you need speed and to cut many types of materials, pick laser cutting.
EDM can make very exact cuts. It uses electrical sparks to take away small bits of metal. This helps you make tiny details. Many companies use EDM for small or tricky parts. EDM is good when you need parts to fit just right. Look at the table to see how close EDM can cut:
EDM Type | Precision Tolerance |
|---|---|
Standard EDM | ±0.01 mm (10 microns) |
High-Precision EDM | ±0.002 mm (2 microns) |
EDM is great for making molds and dies. It is also used for medical device parts. EDM is trusted when every tiny bit counts.
Laser cutting is also very exact, mostly for thin things. The laser beam can cut small shapes and sharp corners. You get smooth lines and nice curves. Laser cutting has trouble with thick things. The heat from the laser can melt or bend the edges. This can make the cut less exact. Here is a table to compare:
Cutting Method | Precision | Best For |
|---|---|---|
EDM Cutting | High precision with tight tolerances | Fine features and intricate details |
Laser Cutting | High precision, struggles with thick materials | Sharp edges and intricate designs in thin materials |
Laser cutting is a good pick for thin sheets. It is fast and makes accurate cuts.
You want your parts to look nice and fit well. Edge quality is important for how things work and look. Laser cutting makes sharp, dark edges on some steels. The CO2 laser burns through the metal for a clean edge. Thicker metal can have more lines or rough spots. Sometimes you need to clean off extra bits, called dross, for a smooth edge. The kind and thickness of the material change how the edge looks.
Tip: Pick the right cutting method for your material and thickness to get the best edge.
Both EDM and Laser Cutting are very exact. Each one is better for different jobs.
When you use EDM, you get very precise cuts, but the process takes time. EDM machines work by sending electrical sparks through a wire or electrode. Each spark removes a tiny bit of metal. You can expect EDM machines to cut up to 250 inches per minute. The actual speed depends on the thickness and type of metal. Here are some key points about EDM cutting speed:
EDM works best for detailed shapes.
The speed slows down for thicker or harder metals.
You get great accuracy, but you need to wait longer for each part.
Tip: EDM is a smart choice when you need perfect details, even if it takes more time.
Laser cutting stands out for its speed, especially with thin materials. The laser beam moves quickly and makes clean cuts. You can use laser cutting for many materials, including stainless steel and aluminum. The speed changes based on the material and its thickness.
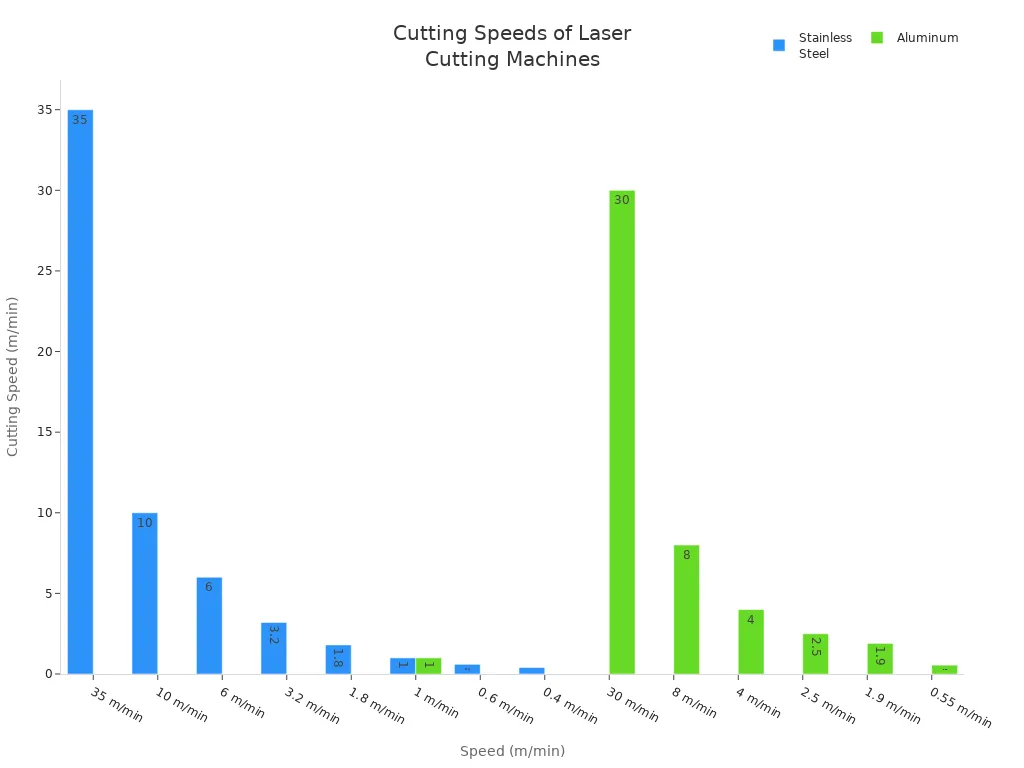
Laser cutting lets you finish jobs quickly. You can cut many parts in less time than with EDM.
When you compare EDM vs. Laser Cutting, you see big differences in production efficiency. EDM works best for low-volume jobs where you need high accuracy. Laser cutting handles high-volume production much better. The table below shows how each method fits different needs:
Method | Production Efficiency | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
Wire EDM | Slower | Best for low-volume jobs |
Laser Cutting | Faster | Handles high-volume production well |
If you want to make many parts fast, laser cutting gives you the edge. If you need a few parts with perfect details, EDM is the way to go.
You can pick EDM or laser cutting based on your material. Wire EDM works best with metals that conduct electricity, like steel, titanium, and aluminum. EDM does not work on plastics, ceramics, or glass. Laser cutting can cut more types of materials. You can use it on metals, plastics, wood, and some composites. But laser cutting has trouble with shiny materials like copper and aluminum. Some dangerous materials are also hard for lasers to cut.
Cutting Method | Suitable Materials | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
Wire EDM | Conductive materials | Non-conductive materials (like ceramics, plastics, glass) cannot be cut. Slow speed makes it hard for big jobs. Large pieces may not fit in the machine. |
Laser Cutting | Metals, plastics, wood | Not as good on shiny materials (like copper, aluminum) and some dangerous materials. |
Tip: Laser cutting is better if you need to cut many different materials.
Wire EDM: You get very exact cuts and can make tricky shapes in metals.
Laser Cutting: You can cut lots of materials, but shiny surfaces can be a problem.
How thick your material is will help you choose the right method. EDM can cut thick metals, but it takes more time. Laser cutting is fast on thin sheets. New fiber lasers can also cut thicker pieces.
Material Type | Max Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|
Stainless Steel | 16 |
Aluminum | 16 |
Yellow Copper | 10 |
Carbon Steel | 20 |
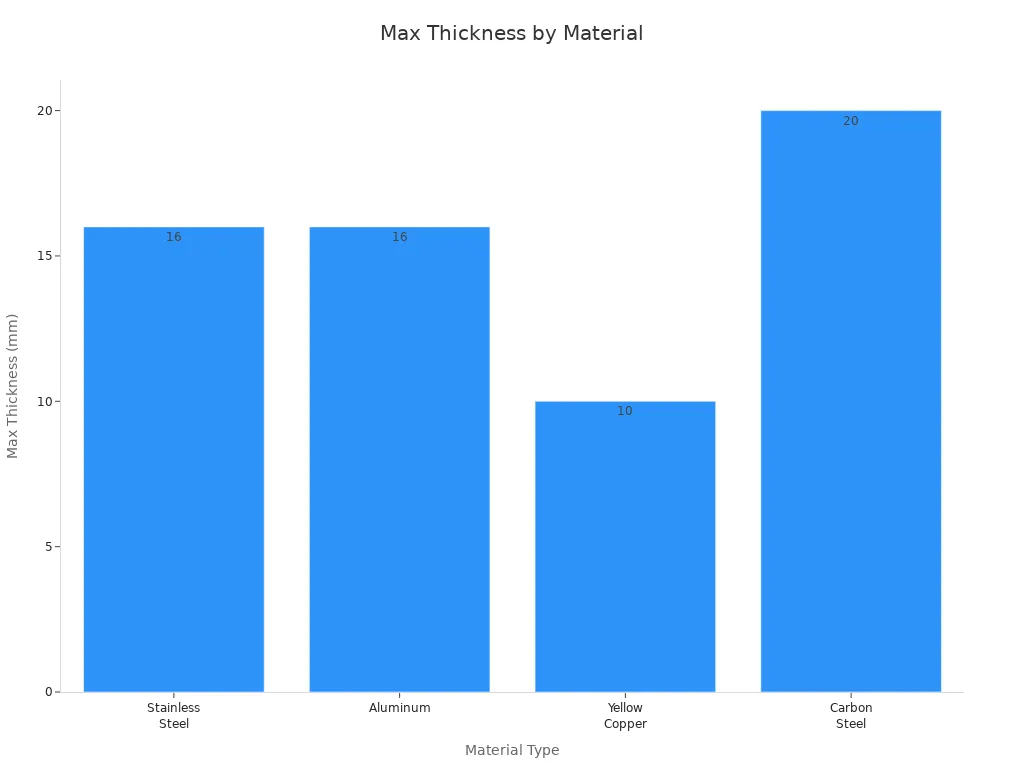
Fiber lasers let you cut even thicker materials:
Material Type | Laser Type | Max Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|
Stainless Steel | Fiber | 25 |
Aluminum | Fiber | 20 |
Brass | Fiber | 15 |
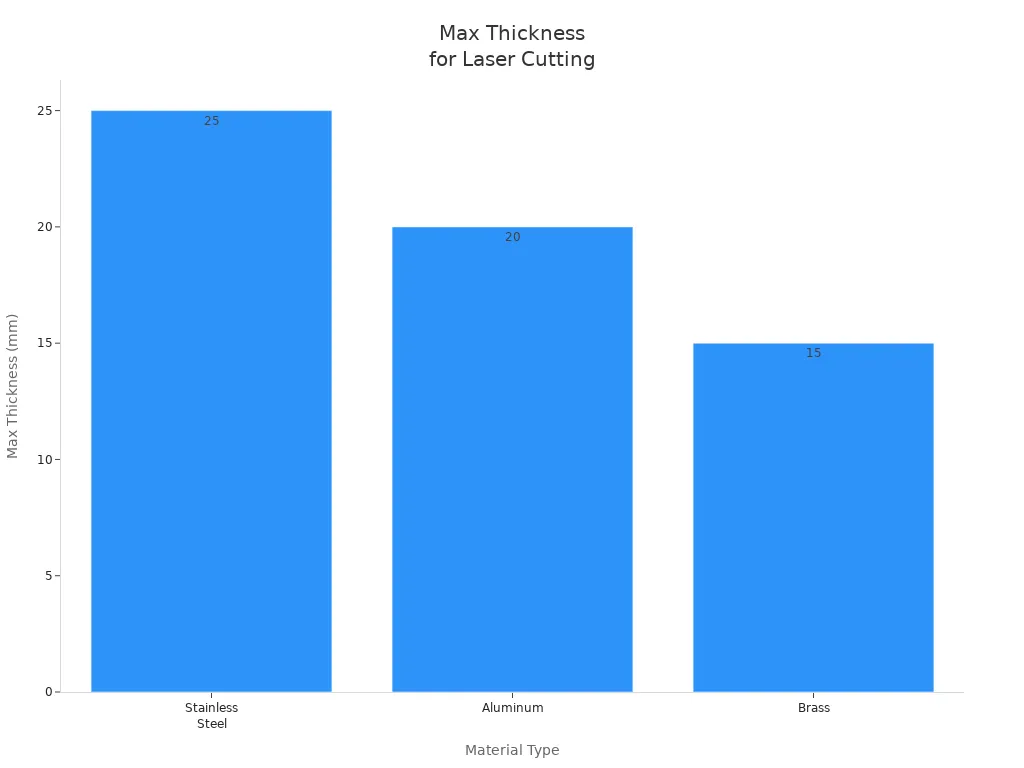
Note: Fiber lasers can cut stainless steel up to 50mm thick. CO2 lasers can cut up to 12mm.
Pick the cutting method that matches your project. EDM is best for making tools, molds, and small batches of tricky metal parts. It gives you very exact cuts and works on hard metals. Laser cutting is good for jobs that need to be done fast and for many types of materials. You can use it for signs, car parts, and things people buy. It also wastes less material.
Cutting Method | Best Suited Applications | Material Properties |
|---|---|---|
EDM | Tooling, molds, small batches of tricky parts | Hard materials, very exact cuts |
Laser Cutting | Signs, car parts, products for people | Fast, flexible, less waste |
If you want perfect details in hard metals, EDM is best. If you need to work fast and cut many materials, use laser cutting.
You need to think about the cost before picking a cutting method. EDM machines cost more at first because they use special technology for very exact cuts. Industrial laser cutters also need a lot of money to buy. Here is how much both types can cost:
Industrial laser cutters start at $250,000 for small models. Strong fiber lasers can cost over $2 million.
CO2 laser machines start at about $15,000. The price goes up if you want more power or a bigger machine.
CNC machines, including laser cutters, cost between £50,000 and £500,000. The price depends on what features you want.
If you need to cut thick metals or want very exact parts, EDM might be worth the higher price. If you need to cut lots of thin parts, a laser cutter can save you money over time.
You also need to think about how much it costs to use each machine. Laser cutting does not use much energy, especially with fiber lasers. The cost to run the machine depends on the type and power of the laser:
CO2 laser cutting machines (80-300W) cost about $0.10 to $0.60 per hour.
Fiber laser machines (1-3 kW) cost $0.90 to $3.60 per hour. Strong fiber lasers (10-60 kW) can cost $26 to $52 per hour.
Skilled workers usually get paid $20 to $50 per hour.
EDM machines use more energy and need special fluids, which makes them cost more to run. But EDM makes less waste because it can reuse and fix electrodes.
Maintenance changes how much you spend and how fast you work. EDM machines need a lot of care to keep working well. You have to check the electrodes, fluids, and parts often. Laser cutting machines do not need as much care. You mostly clean the optics and change filters.
Cutting System | Maintenance Requirement |
|---|---|
EDM | Frequent maintenance required |
Laser Cutting | Less maintenance required |
Tip: Take care of your machines often so they do not break down and last longer.
If you only make a few special parts, EDM gives you very exact cuts and does not waste much material. If you make a lot of parts, laser cutting can save you time and money, even if it costs more at first. Pick the method that fits your project size, material, and design. Laser cutting is best for making lots of thin parts. EDM is better for small jobs or tricky metal parts.
EDM is used when you need very exact metal parts. Many industries pick EDM because it can make hard shapes. Here are some ways EDM is used:
Turbine blades for jet engines
Surgical tools for hospitals
Fuel injector parts for cars and trucks
Plastic molds for making products
Gemstone holders for jewelry
Gears and splines for machines
Stamping and punching tools for factories
Medical implants for patients
EDM helps make parts that must fit just right. In airplanes, EDM shapes turbine blades to work better. Car makers use EDM for gears and molds. Electronics companies use EDM for tiny, detailed parts. Hospitals and medical companies use EDM for tools and implants that need to be very exact.
Laser cutting is fast and can cut many shapes. You can use it on lots of materials. This makes laser cutting popular in many jobs. Here is a table that shows where laser cutting is used:
Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
Automotive | Body panels, strong steel parts, car frames |
Safety parts, turbine blades, engine pieces | |
Electronics | Tiny parts, silicon chips, circuit boards |
Medical | Test equipment, surgical tools, metal covers |
Construction | Big parts, plates, bridges, tunnels |
Military | Armor plates, marking gear, weapon parts |
Laser cutting can make car doors and airplane parts. It also cuts small pieces for electronics. Hospitals use laser cutting for tools and equipment. Builders use it for big things like bridges. The military uses laser cutting for strong, safe parts.
EDM and laser cutting are used in many jobs today. Car companies use laser cutting for doors and panels. Electronics makers use laser cutting for circuit boards. Airplane companies use both EDM and laser cutting for engine parts. Hospitals and medical companies use EDM for implants and laser cutting for equipment. Metal shops use laser cutting to shape metal sheets. Builders use laser cutting for big metal parts. The military uses both methods for strong, exact parts.
Tip: Think about what your industry needs before you choose EDM or laser cutting. Each one is best for different kinds of work.
When you choose between EDM and laser cutting, you need to look at several important factors. Each method works best for different jobs. The table below shows how EDM and laser cutting compare on key decision points:
Decision Factor | Wire EDM | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|
Material Type | Best for hard metals like tool steel and titanium | Cuts metals, plastics, acrylic, and wood. Best for thin to medium thickness. |
Precision and Complexity | Superior precision for complex shapes | Excellent precision, ideal for clean edges on less dense materials. |
Cutting Speed and Volume | Slower, good for small projects or low volume | Faster, great for high-volume, quick-turnaround jobs. |
Cost and Budget | Lower cost for small runs, but maintenance adds up | Higher initial cost, but saves money in large-scale production. |
Tip: Think about your material, the level of detail you need, and how many parts you want to make. These factors help you pick the right method.
Your project needs will guide your choice. Here are some points to help you decide:
Cutting Speed: Laser cutting works much faster than EDM. You should use laser cutting if you need to make many parts quickly.
Precision: EDM gives you the best precision. Choose EDM for tight tolerances or detailed shapes, especially in thick materials.
Material Thickness: Laser cutting handles thin to medium materials well. EDM works better for thick or hard metals.
If you want to cut many thin parts from different materials, laser cutting is a strong choice. If your project needs perfect details in hard or thick metals, EDM will serve you better.
Remember: The right method depends on your project’s needs. Take time to match your job with the strengths of each cutting process. This way, you get the best results for your manufacturing goals.
Laser cutting is quick and can do many jobs. It does not cost a lot to set up. EDM is best when you need very exact metal parts. But each method has things it cannot do. Laser cutting does not work well on thick or shiny materials. EDM takes more time to finish a job. Before you pick one, look at what your project needs:
Project details
How much money you have
How hard the part is to make
How many parts you need
Decide what is most important for your job. Do you want it to be exact, fast, or cheap? To get the best outcome, tell an expert about your part and what you want. You can also ask for a price quote to begin.
EDM can cut metals like steel, titanium, and aluminum. Laser cutting works on metals, plastics, wood, and some ceramics. EDM only cuts materials that can carry electricity. Laser cutting can cut more things but has trouble with shiny metals.
EDM makes very smooth and exact edges, even on thick metals. Laser cutting also makes clean edges, but thick materials may look rough. You usually do not need to fix edges much after using EDM.
Laser cutting uses a strong light, so you must wear eye protection. EDM uses electricity and special fluids, so you must follow safety rules. Both are safe if you use the right gear and follow the steps.
Think about what material you have, how thick it is, and how many parts you need. Use EDM if you want high precision in hard metals. Pick laser cutting if you want speed and to cut many types of materials.
Navigation
Navigation
Contact Us
Tel: +86 13417419143
E-mail: [email protected]
Add:
2nd Floor, Building 7, 156 High Tech Industrial Park, Fuyuan 1st Road, Zhancheng Community, Fuhai Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen City, China.