Sep.
02, 2025
Contents
CNC Machining Titanium: Properties & Applications

You often see titanium in CNC Machining Titanium because it has special properties. Titanium is strong but not heavy. It does not rust easily. It can handle very hot or cold temperatures. Titanium is also safe for the human body. This makes it good for medical implants.
Aerospace: Strong but light and works in hot or cold places
Medical: Safe for the body and does not rust in implants
Automotive: Light and tough parts for fast cars
Titanium can do many things. It meets the tough needs of these industries and others.
Many industries pick titanium for CNC machining. Titanium is special because it is strong and light. It can handle tough places without breaking. When you use CNC Machining Titanium, the parts are strong but not heavy. This is why airplanes, race cars, and medical implants use it.
Here are the main reasons titanium is good for CNC machining:
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Strength and Lightweight | It is very strong but does not weigh much. This helps when weight matters. |
Corrosion Resistance | It does not rust easily. It works well in salty water. |
Biocompatibility | It is safe for the body. Doctors use it for implants and prosthetics. |
Resilience in Heat | It can take a lot of heat. It is good for things like jet engines. |
Cost Considerations | It costs more, but it lasts a long time. This can save money later. |
CNC Machining Titanium gives you many good things:
The parts last a long time, even in hard places.
Titanium does not rust or get damaged by water or chemicals.
Medical tools made from titanium are safe inside people.
Titanium keeps its shape and strength, even when it gets hot.
But, CNC Machining Titanium costs more than using aluminum or steel. There are a few reasons for this:
Titanium is more expensive to buy and work with.
Machining takes longer because you must go slow.
Tools break faster, so you need new ones more often.
Sometimes, you need extra steps to make the parts look nice.
Even though it costs more, many people still use titanium. Its good points are worth the extra money.
Titanium makes parts strong but not heavy. It is lighter than steel. Titanium is about 56% lighter than stainless steel. It is also twice as strong. You can use less titanium and still get good strength. Many industries pick titanium for this reason. Airplanes, cars, and sports gear use titanium to save weight.
Tip: Lighter parts help machines go faster and use less power.
Titanium does not rust or get damaged by chemicals. It has a natural layer that protects it. This layer keeps titanium safe in tough places.
Material | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|
Titanium | Excellent |
Stainless Steel | Depends on alloy (Good resistance) |
Aluminum | Good |
Titanium works better than stainless steel and aluminum in hard jobs.
Stainless steel needs enough chromium to resist rust.
Aluminum has a layer too, but it may not last as long as titanium.
Titanium is great for marine, chemical, or outdoor jobs. It keeps parts safe and working longer.
Titanium is safe for medical tools and implants. Doctors use titanium because it does not react with the body. It resists rust better than stainless steel and cobalt-chromium alloys. Titanium lasts a long time inside the body.
Titanium is used for bone screws, joint parts, and dental implants.
Its safety means fewer problems for patients.
Titanium gives both safety and strength.
Titanium stays strong when it gets hot. You can use it in engines and turbines. Titanium alloys work well in both cold and hot places. The table shows how titanium works at different temperatures:
Temperature (°C) | Mechanical Properties Maintained |
|---|---|
-25.7 | Notched tensile strength ratio of 0.95-1.15 |
195.5 | Good ductility and toughness |
252 | Works for alloys with low gap elements |
450-481 | Lasts long for general industrial alloys |
540 | Lasts a short time for general industrial alloys |
600 | Special titanium alloys for high heat |
760 | Short-term use for missile parts |
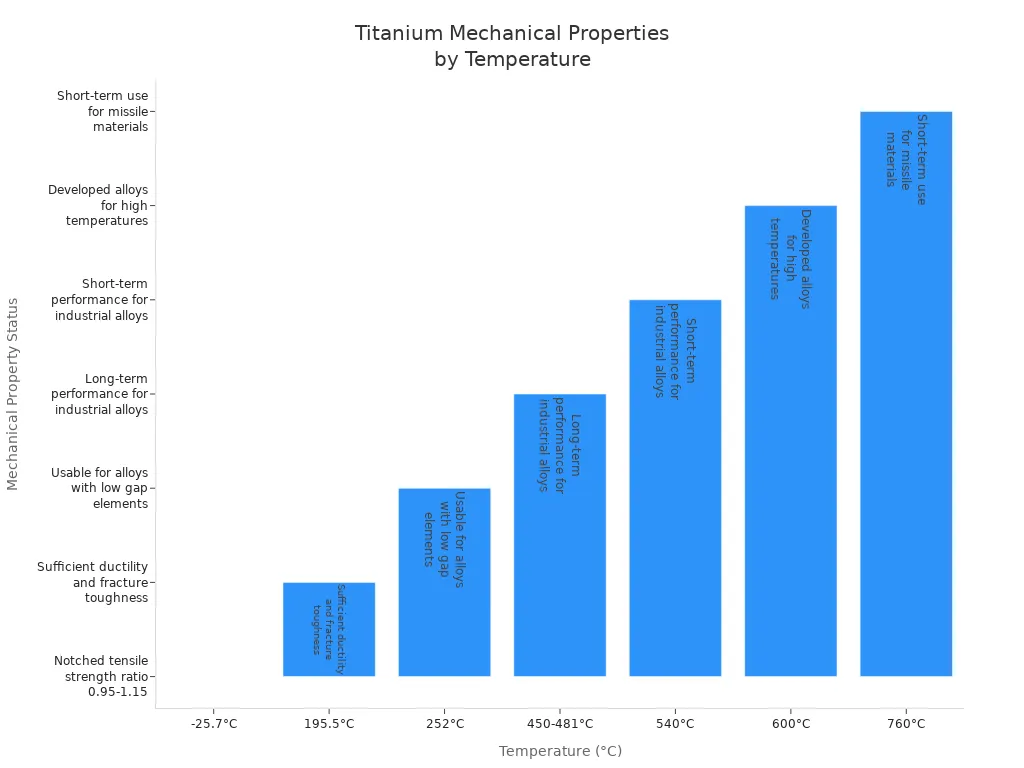
Titanium stays tough even when other metals fail. This makes it good for CNC Machining Titanium parts that work in extreme heat or cold.
Grade 1 titanium is easy to bend and shape. It has the highest purity of all grades. This grade is soft and resists rust well. You can use Grade 1 for parts that need welding or forming. Many industries pick Grade 1 when high strength is not needed.
Common uses for Grade 1 titanium include:
Exhaust systems
Aerospace components
Bicycle frames
Fishing gear
Marine hardware
Grade 1 is good when you need parts that bend and do not rust.
Grade 2 titanium is stronger than Grade 1. It is still easy to shape and machine. You see Grade 2 in chemical plants and marine parts. It also works in heat exchangers. This grade does not rust and can handle tough jobs.
You can machine Grade 2 with less tool damage than harder grades. It is a good pick for parts that need to last but are not under heavy stress.
Grade 5 is also called Ti-6Al-4V. It is the most used titanium alloy for CNC machining. Grade 5 is very strong and does not rust. It is also easy to machine. You find Grade 5 in aerospace, medical, and car parts. It is used for parts that must be light and strong.
Machining Grade 5 needs slow cutting and good cooling. Wet or cryogenic cooling helps tools last longer. Studies show cryogenic cooling can double tool life compared to dry machining.
Tip: Grade 5 is best for parts that need high performance.
Here is a table to compare the main titanium grades:
Titanium Grade | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | High strength, corrosion resistance, good machinability | Aerospace, medical, automotive |
Grade 2 (Commercially Pure) | Easier to machine, good corrosion resistance | Lower strength requirements |
Cooling and lubrication are important when machining titanium. Dry machining makes tools wear out faster by 18%. Using minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) helps tools last longer by 19%. Cryogenic cooling can make tools last twice as long. Pick the right grade and cooling method for your job.
Picking the right titanium grade helps you get the best results. Grade 5 is strong and lasts long. Grade 2 is easier to machine. Grade 1 is best for bending and rust resistance.
When you machine titanium, heat becomes a big problem. Titanium does not move heat away from the cutting area. Its thermal conductivity is much lower than aluminum or steel. This means the cutting edge of your tool gets extremely hot—sometimes over 1,000°C. The heat stays trapped at the tip, which can cause the tool to soften and lose its sharpness. You may also see bits of titanium stick to the tool, a problem called galling.
Tip: Always use high-pressure coolant (at least 1,000 PSI) and aim it right at the cutting edge. Keep your feed rates steady and avoid stopping the tool in one spot. Try to use dynamic milling strategies and keep the tool moving to help manage heat.
Titanium’s high strength makes it tough on your cutting tools. You need to use more force to cut it, which wears down the tool faster. The heat that builds up at the cutting edge makes this even worse. At high temperatures, titanium can react with the tool, causing it to wear out quickly.
Here are some tool options that help reduce wear:
Cutting Tool Type | Key Features |
|---|---|
Carbide cutting tools | High hardness, good wear resistance, and toughness |
Coated tools (Al2O3, TiAlN) | Special coatings reduce heat transfer and prevent galling |
Polycrystalline cubic boron nitride | Excellent for high-speed cutting and thermal stability |
Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools | Extremely hard and wear-resistant, but expensive |
Change your tools often and use the right coatings to make them last longer.
Titanium can harden as you machine it. This makes the next cut even harder and can affect the final size and smoothness of your part. If you let the tool rub instead of cut, the surface gets even tougher. This can make it hard to keep tight tolerances, especially for parts that need high precision.
Work hardening can cause your part to drift out of tolerance.
Dimensional accuracy may change during long machining cycles.
For best results, machine titanium when it is in its softest state.
Keep your cutting speeds low and your feed rates high enough to avoid rubbing. This helps you get a better finish and keeps your parts accurate.
Choosing the right tool makes a big difference when you machine titanium. You want tools that can handle heat and tough material. Carbide tools work best because they stay sharp and strong. Tools with five or more flutes help you remove material faster. Special coatings like TiAlN protect your tool from heat and wear.
Pick carbide tools made for titanium.
Use tools with many cutting edges for smoother cuts.
Choose coatings like TiAlN to keep your tools cool and lasting longer.
Regularly check your tools for wear or bending. Replace them before they break to keep your parts accurate.
Coolant keeps your tools and titanium cool during machining. High-pressure coolant works best because it pushes heat away fast. You need to keep coolant flowing all the time when the tool touches the titanium. This helps stop chips from sticking and keeps the cutting area clean.
Coolant Type | Cooling Potential |
|---|---|
Water | Very High |
Ammonia | Moderate |
Ethanol | Moderate |
Liquid Nitrogen | Baseline |
Liquid Carbon Dioxide | Low |
Use high-pressure coolant to lower heat.
Make sure chips leave the cutting area right away.
Keep flutes clear to avoid galling and tool damage.
Ample coolant helps you manage titanium’s sticky nature and keeps your tools working longer.
Setting the right cutting speed, feed, and depth helps you get the best results. You want to use slower feed rates than you would for steel. Higher spindle speeds help reduce heat. Lower radial engagement keeps your tool from overloading.
Operation Type | Cutting Speed (m/min) | Feed per Tooth (mm) | Depth of Cut (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
Roughing | 40-60 | 0.1-0.15 | 2-4 |
Semi-finishing | 60-80 | 0.08-0.12 | 1-2 |
Finishing | 80-100 | 0.05-0.08 | 0.5-1 |
Use slower feed rates—about one-third to one-half of steel.
Check your tool often for wear.
Keep radial engagement low (5-15% of tool diameter).
Good cutting parameters help you avoid heat buildup and keep your parts precise.
There are different ways to finish titanium parts after CNC machining. These ways help you get the surface you want. Each method is good for certain jobs.
Grinding uses a rough wheel. It makes surfaces smooth or shapes parts with care.
Sanding takes away small bumps. You use rough materials to make the surface flat.
Bead blasting shoots tiny glass beads at the part. This removes marks and gives a dull look.
Polishing uses rough stuff or chemicals. It makes the part shiny like a mirror.
If you want a shiny part, polishing is best. For a dull look, bead blasting works well.
Chemical treatments change the outside of titanium. These treatments make it stronger and help it last longer. They also make parts look better.
Blackening puts a dark layer on the part. This stops rust and makes it shiny.
Anodizing adds a strong layer on top. It stops rust and lets you pick colors.
Thermal spraying covers the part with a hard coat. This keeps the surface safe from harm.
Chemical treatments help titanium parts last and look nice. Pick the one that fits your needs.
Anodizing gives many good things when you finish titanium parts. It makes parts stronger, safer, and better looking.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Corrosion Resistance | Anodizing helps titanium parts fight rust. |
Wear Resistance | The surface gets tougher and lasts longer. |
Aesthetic Appeal | You can pick many colors for a cool look. |
Biocompatibility | Anodized parts are safe for medical use. |
Thermal Insulation | Anodizing helps keep heat away. |
Cost-Effectiveness | It is not expensive and makes parts last longer. |
Environmental Friendliness | Anodizing is safe for the environment. |
Anodizing also makes parts less slippery, so they do not stick. Anodized titanium stays clean and safe for people. You can choose from many colors to tell parts apart. The process keeps the surface safe from electricity and dirt.
Anodizing helps titanium parts last, look nice, and stay safe in hard places.
Titanium is used a lot in aerospace. Planes need parts that are strong and light. Titanium helps planes go faster and use less fuel. You can find titanium in jet engine blades and seat frames. It is also in turbine shafts and oxygen system parts. Titanium does not get damaged by heat or stress. This makes it good for engines and wings. CNC Machining Titanium helps make accurate parts for these jobs.
Titanium helps planes stay safe and work well. The parts last longer and weigh less.
Hospitals use titanium for many tools and devices. You see titanium in joint replacements and bone screws. It is also in dental implants. Doctors like titanium because it does not react with the body. CNC Machining Titanium makes parts that fit well and stay strong inside people.
Some medical devices made from titanium are:
Stethoscopes
Ventilator parts
EKG, X-ray, and MRI machines
Blood pressure monitors
Catheters
Stretchers and hospital beds
Defibrillators
Prostheses
Joint replacements
Spine screws and rods
Pacemakers
Drug delivery devices
Coronary stents
Surgical scissors
Scalpels
Forceps
Clamps
Retractors
Dental probes and scalers
Dental mirrors
Dental drills
Suction devices
Titanium helps patients heal faster and stay safe. Medical parts made from titanium last for many years.
Titanium is used in many military vehicles and equipment. It is as strong as steel but much lighter. This helps planes and armored vehicles move faster and use less fuel. Titanium does not rust, so it works well in ships and submarines. It also stands up to high heat and stress in missiles and engines.
Military engineers use titanium in:
Aircraft exteriors and engines, like the SR-71 Blackbird and F-22 Raptor
Naval vessels, including exhaust stack liners and submarine piping
Armor for vehicles, which protects soldiers and keeps vehicles easy to drive
Titanium alloys must be strong and light. They need to resist heat and fatigue. You get parts that work well in tough combat situations.
Car makers use titanium for high-performance parts. Titanium makes cars lighter and faster. You find titanium in engine valves and suspension springs. It is also in brake caliper pistons and connecting rods. Race cars use titanium for parts that need to be strong but light. CNC Machining Titanium helps make parts that fit engines and brakes very well.
Titanium parts help cars go faster and last longer. You spend less time fixing and more time driving.
Boats and ships need parts that can handle saltwater. Titanium does not rust in the ocean. It forms a layer that heals itself if scratched. You find titanium in propeller shafts and underwater robots. It is also in rigging, ball valves, heat exchangers, and fire system piping.
Titanium resists saltwater better than steel.
It keeps its strength even when waves hit hard.
You get lighter parts that need less fixing.
Titanium saves money over time because you do not need to replace parts often.
Titanium works in special jobs where you need high performance. You see it in heat exchangers and shells. It is also used for precision components. CNC Machining Titanium helps make parts for important environments.
Industry | Specialized Uses |
|---|---|
Marine and Naval | Propeller shafts, underwater robotics, rigging equipment, ball valves, marine heat exchangers, fire system piping, pumps, exhaust stack liners, onboard cooling systems |
Aerospace | Seat components, turbine parts, shafts, valves, housing, filter components, oxygen generation system parts |
Automotive | Valves, valve springs, retainers, car stop brackets, hanging ear nuts, engine piston pins, suspension springs, brake caliper pistons, engine rockers, connecting rods |
Medical and Dental | Bone screws, dental implant screws, cranial screws, spinal fixation rods, connectors, plates, orthopedic pins |
Titanium parts work in places where other metals cannot. You get good performance in extreme heat, cold, and stress.
Titanium is special in CNC machining. It is strong and light. It does not rust or get damaged by heat. You should learn about its special features and the problems it can have. Many industries use CNC machined titanium for important parts. Aerospace, medical, and automotive companies trust it.
If you want parts that last long and stay strong, titanium is a good pick. It works well in hard places and is smart for your project.
Titanium costs more because it is tough and wears out tools quickly. You need slower speeds and special coolants. You also replace tools more often. These steps add to the total cost.
You can use standard CNC machines for titanium. You need strong tools and good cooling. Carbide tools work best. Always check your machine for wear after each job.
You can use polishing, bead blasting, or anodizing. Polishing gives a shiny look. Bead blasting makes the surface dull. Anodizing adds color and protects the part.
You find titanium parts in airplanes, medical implants, race cars, and ships. These industries need strong, light, and rust-free parts. Titanium works well in tough places.
Titanium is safe for your body. Doctors use it for bone screws, joint replacements, and dental implants. It does not react with tissue. Patients heal faster and stay healthy.
Navigation
Navigation
Contact Us
Tel: +86 13417419143
E-mail: [email protected]
Add:
2nd Floor, Building 7, 156 High Tech Industrial Park, Fuyuan 1st Road, Zhancheng Community, Fuhai Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen City, China.