Oct.
28, 2025
Contents
Understanding Production Cycle Time in CNC Machining

Production Cycle Time in CNC machining tells you how long it takes to finish one job from beginning to end. If you know and improve this time, your work gets quicker and smoother. You also spend less money and make more products.
Shorter cycle times save money when making things.
Making things faster means you make more.
Using machines and better tools helps you work better and pay workers less.
If you watch cycle time carefully, you plan better and keep your work on schedule.
Production Cycle Time in CNC machining tells how long it takes to finish one job. You start counting when the machine starts working on a part. You stop counting when the part is done. Experts say production cycle time is the total time for one or more steps. This number shows how fast your machines work. It also shows how much you can make in a set time. You use this number to check how well you are doing. It helps you plan your work and control spending. When you know your production cycle time, you can plan jobs better. You can order materials and set budgets with more trust.
People sometimes talk about lead time and cycle time. These words sound alike but mean different things. The table below shows how they are not the same:
Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Lead Time | The total time a customer waits for an order from start to finish, including all steps. |
Cycle Time | The time it takes to finish one part, showing how things work right now. |
You need to measure production cycle time the right way if you want your shop to work well. When you watch this number, you can find problems and fix them fast. Good measuring helps you in many ways:
Cost Estimation: You can guess how much each part will cost, including all costs.
Production Planning: You can plan jobs better and stop slowdowns.
Resource Allocation: You can give machines and workers the right jobs.
Quality Control: You can make sure there is time to check quality, so there are fewer mistakes.
Improved Customer Satisfaction: You can give customers good delivery dates, which makes them happy and helps you do better than others.
Supply Chain Efficiency: You can help just-in-time making and keep your supply chain working well.
Tip: When you pay attention to production cycle time, your shop works better and can beat others. Even small changes can save money and make things faster.
If you know and watch production cycle time, you can make better choices every day. This helps you keep your shop on time, spend less, and give good parts to your customers.
You need to know the right formula to find out how long it takes to make one good part. The most common way is:
Cycle Time = Net Production Time / Good Units
Net Production Time means the total time your machine spends making parts, not counting breaks or downtime. Good Units means the number of parts that meet your quality standards.
You can also use other formulas to help you understand each step in the machining process. The table below shows some formulas you might use in CNC machining:
Formula Description | Formula |
|---|---|
Length | Tool Approach + Job Length + Tool Over Travels x Number of Passes |
Average Revolutions Per Minute | 1,000 x Cutting Speed / π x Average Diameter of Rod (mm) |
Machining Time | Length of Cut (mm) / Feed (mm per revolution) x Revolutions Per Minute |
Revolutions Per Minute | 1,000 x Cutting Speed (mm per minute) / π x Diameter of Rod (mm) |
Machining Time | Length of Cut (mm) / Feed (mm per revolution) x Revolutions Per Minute |
These formulas help you break down each part of the job. You can use them to check your numbers and make sure your machine works as fast as it should.
Let’s look at a simple example. You want to mill a groove in a metal part. Here is how you can find the cycle time:
Gather the Right Inputs
You need to know the tool diameter, spindle speed, feed rate, depth of cut, length of tool path, number of passes, and any non-cutting time.
Define the Machining Operation
Suppose you want to mill a 200 mm groove, 4 mm deep, in two passes. Your feed rate is 400 mm/min, and your spindle speed is 3,000 RPM.
Use the Milling Formula
Machining Time (min) = Length of Cut ÷ Feed Rate
For one pass:Machining Time = 200 mm ÷ 400 mm/min = 0.5 minutes
You need two passes, so total cutting time is 1 minute.
Add Non-Cutting Time
Sometimes you need extra time for tool retraction or moving the tool into position. If this takes 0.33 minutes, your total machining time is 1.33 minutes (or 1 minute, 20 seconds).
Tip: Always include non-cutting time when you calculate Production Cycle Time. This gives you a more accurate number.
You can measure cycle time by timing your machine from the moment it starts working on a part until the part is finished. Use a stopwatch or your CNC machine’s built-in timer. Write down the start and end times for each part. Do this for several parts to get an average. This helps you spot problems and improve your process.
You might run into some common errors when you measure cycle time:
Programming errors can happen if you enter the wrong data into your CNC controller. This can cause big problems and slow down your work.
Sub-optimal feed and speed settings can make your parts look bad or wear out your tools faster. If you set the speed too high, your tool can bend or break. If you set the feed too low, you waste time.
Note: Check your numbers often. Fix mistakes quickly to keep your shop running smoothly.
If you measure and understand cycle time, you can make better choices. You can plan your jobs, save money, and make sure your parts meet quality standards.
Your CNC machine’s strength and accuracy play a big role in how fast you can finish a part. If your machine is not rigid, it can vibrate or heat up, which causes errors and slows down your work. You can solve this by choosing machines made from materials that resist heat and by keeping the shop at a steady temperature. When your machine stays steady, you get better parts and avoid extra work.
Modern CNC machines use smart controllers. These controllers run programs quickly and keep downtime low. They also adjust feed rates as needed, which helps your tools last longer and keeps your parts looking good. With high-speed processors, your machine can move all its axes at once, making smooth cuts and saving time.
Tip: A rigid, precise machine with a good controller helps you make more parts in less time.
The tools you pick for your CNC machine change how fast you can work. The right tool lets you cut faster, take deeper cuts, and finish parts with fewer tool changes. If you use tools made for your material, you can run at higher speeds and feed rates.
Cutting tools designed for certain materials let you work faster.
Good tool shapes help you move through the material quickly.
Tools that handle deeper cuts save time on each pass.
Tool wear also matters. Worn tools slow you down, make rough surfaces, and can even break. You should check your tools often and replace them before they cause problems.
The type of material you use affects your cycle time. Some materials cut easily, while others take more time and care. Look at the table below to see how different materials can change your machining speed:
Material Type | Characteristics | Cycle Time Impact |
|---|---|---|
Plastic (e.g., ABS) | Low cutting force, less heat, high speeds and feed rates | Fast machining, aggressive cutting possible |
Aluminum Alloys | Easy to machine, high removal rates | Great for quick jobs, short cycle times |
Stainless Steel | Needs slow speeds, careful cooling | Slower machining, longer cycle times |
Tool Steel | Hard, needs special tools and settings | Longest cycle times, more tool changes |
Advanced Polymers | Needs special handling | Can be fast with right setup, good surface finish |
You control cycle time by setting the right speed, feed rate, and depth of cut. Higher speeds and feed rates remove material faster, but they can wear out your tools quickly. Deeper cuts save time, but only if your tool and machine can handle it.
Speed (vc) | Depth of Cut (ap) | Machining Time |
|---|---|---|
High | Shallow | Short |
Moderate | Medium | Balanced |
Low | Deep | Longer |
Note: Always balance speed and tool life. Fast settings save time, but worn tools can slow you down or ruin parts.
If you choose the right machine, tools, materials, and settings, you can make your CNC shop faster and more efficient.
You can draw a map of each step in your CNC machining process. This helps you see where you waste time or materials. When you look at your workflow, you find steps that do not help. You also find places that slow you down. The table below shows how mapping your process can make cycle times shorter:
Evidence | Explanation |
|---|---|
Process Mapping | Finds steps and slow spots that are not needed in making things. |
Reduced Cycle Time | Checking steps helps you make changes for faster cycles. |
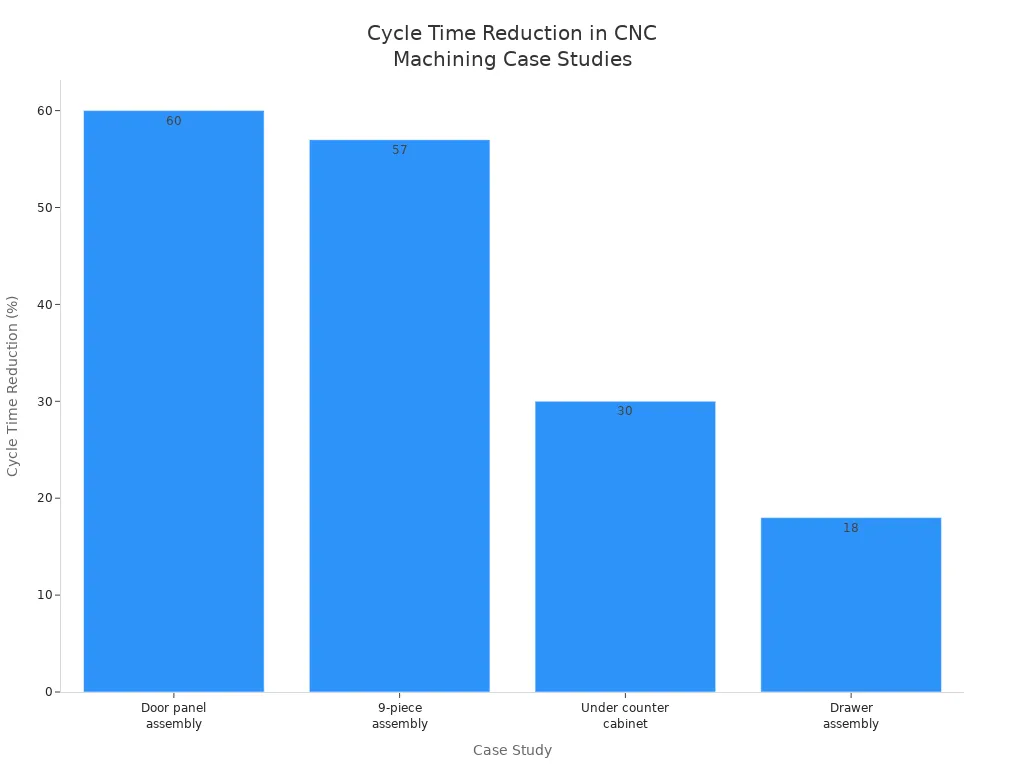
Many companies use process mapping to change their products and how they work. For example, one company made a door panel with only one part instead of five. This made the cycle time 60% shorter. Another company made a nine-piece assembly into one piece and cut cycle time by 57%. You can see more results in the chart below:
You should look for waste in your process. Waste can be extra material, wasted energy, or lost time. The table below lists common types of waste:
Type of Waste | Description |
|---|---|
Material Waste | Extra material thrown away after machining. |
Energy Waste | Too much electricity used because of bad practices. |
Time/Process Inefficiencies | Time lost from slow or poor processes. |
When you get rid of waste, your shop works faster and costs less. One company used machines and better planning to cut cycle time from 120 seconds to 90 seconds per part. This made machining time 30% shorter and machines worked 15% better. The cost to make things dropped by 10%.
You can make cycle times more steady by making your steps the same each time. If you use the same tool holders or set the same speeds, you spend less time setting up and fixing mistakes. One airplane company saved 15% on setup time and made parts 10% better by using the same tool holders. Studies show that if your steps are not the same, you can have up to 20% more scrap and rework.
Best ways to standardize include:
Set the best spindle speeds and feed rates.
Use toolpaths that change as needed.
Use automation that works well.
Cut cycle times by up to 45%.
Make tools last over 35% longer.
Automation helps you work faster and make fewer mistakes. Machines can load and unload parts, use bar feeders for steady supply, and robot arms for tool changes. Automated CNC machines can run all day and make more parts for less money. Tools like rotary tables let you work on many sides of a part in one go, which saves time and makes parts more accurate.
Even small changes in your steps can help a lot. If you map your process, remove waste, make steps the same, and use automation, you will get faster cycle times and make more parts.
If you learn about production cycle time, your CNC shop can work better. Measuring this time helps you find slow spots and fix them quickly. Things like tool changes, setting up machines, and programming can change how fast you finish each part.
Cycle time counts both making and setting up parts.
How fast the machine moves, tool swaps, and good programming all matter.
Using better software and strong tools helps you finish faster.
To get better, try these ideas:
Make tool paths and spindle speeds work their best.
Get new cutting tools that work faster.
Use machines to do more steps instead of people.
Check parts while making them to keep quality high.
Teach workers to be quick and do things the same way.
Check your cycle times often. Shops that look at their numbers a lot find slow steps and can save hours on each group of parts. Even small changes can help you save time and money.
Cycle time shows how long you need to make one part. Lead time tells you how long a customer waits for the whole order. You use cycle time to improve your shop’s speed.
You can use a stopwatch or your CNC machine’s timer. Start timing when the machine begins work. Stop when the part is finished. Write down the times for several parts to find the average.
Worn tools cut slower and may cause mistakes. You need to stop and change them more often. This adds extra time to your process and can lower your shop’s output.
Automation helps you work faster and make fewer mistakes. You still need to check if your process fits automation. Some jobs need special setups or hands-on work.
You can map your process, remove waste, use the right tools, and add automation. Small changes in setup or tool paths can save you a lot of time.
Navigation
Navigation
Contact Us
Tel: +86 13417419143
E-mail: [email protected]
Add:
2nd Floor, Building 7, 156 High Tech Industrial Park, Fuyuan 1st Road, Zhancheng Community, Fuhai Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen City, China.