Dec.
30, 2025
Contents
What is CNC Routing? An Everything-You-Need-to-Know Guide
Getting Started with CNC Routing

CNC Routing uses computers to move a cutting tool in exact ways. You can make detailed shapes, engravings, or holes in wood, plastic, or metal. This method helps you get results that are correct every time. Makers, hobbyists, and professional manufacturers like HRDJM use CNC Routing to create things. They use it for custom signs, furniture, or models.
You use CNC Routing to cut, carve, and shape materials with computer control. This process lets you create parts with high accuracy and repeatability. You can make simple or complex shapes for many projects. CNC Routing works well for wood, plastic, and metal. You get consistent results every time you run a job.
CNC Routing stands out because it offers:
Precise cuts and engravings
The ability to repeat designs without mistakes
Fast production with less manual work
You can rely on CNC Routing for projects that need detailed shapes. Industries like aerospace and automotive use it for parts that must fit perfectly. You also see CNC Routing in sign making, furniture, and art.
Here are some key principles that define CNC Routing:
You achieve a high degree of accuracy and repeatability.
You can contour complex shapes for advanced applications.
Standard tooling makes the process easier and keeps your workspace organized.
You get consistent cycle times, so each part takes about the same amount of time.
Less manual intervention means you can produce more parts quickly.
You start with a design. You use computer software to create or import the shape you want to cut. The process uses three main software stages:
CAD (Computer-Aided Design): You draw or import the part you want to make.
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing): You set up the toolpaths, choose the cutters, and create the instructions for the machine.
Controller Software: You send the instructions to the CNC router, which follows them to cut your material.
The CNC Routing process follows these steps:
Material Setup: You secure your material on the router bed. Clamps or vacuum tables hold it in place.
Tool Selection: You pick the right router bit for your material and the type of cut you need.
Spindle and Feed Settings: You adjust the spindle speed and feed rate. These settings depend on your material and the bit you use.
Test Cuts: You run a small test cut. This step helps you check the accuracy and quality before you start the full job.
Full Production Run: You let the machine follow the toolpath. You watch for chip removal and make sure the machine runs smoothly.
Tip: Always monitor your CNC Routing job. You can catch problems early and keep your parts looking great.
You find different types of CNC routers for various needs:
Hobby CNC routers work well for small projects and DIY tasks.
Mid-level routers suit small businesses and offer more features.
Industrial routers handle large materials and high-volume jobs.
CNC Routing gives you control over every step. You can make one part or hundreds, and each will match your design.
You use a computer and controller to run a CNC router. The controller is the brain of the machine. It reads instructions from your design software. Then, it tells the router how to move. There are different control systems you can pick. Some use industrial controls. These are very reliable and precise. Others use consumer electronics. These cost less but may not be as accurate.
Control System Type | Characteristics | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
Industrial Controls | Bus-based, 24V logic, high reliability | High precision and reliability, higher cost |
Consumer Electronics | Pulse-based, 3.3V-12V logic, lower reliability | Simpler, cost-effective, less accuracy |
Closed-loop systems use feedback to fix mistakes. They give you more precision. Open-loop systems are easier and cheaper. But they may not be as accurate. You should look at different control systems. Pick the one that fits your needs best.
The spindle is the part that cuts the material. You can choose air-cooled or water-cooled spindles. Air-cooled spindles are easy to set up and care for. Water-cooled spindles stay cool during long jobs. They work better for big projects. There are different spindle types for different materials. GDZ spindles are good for wood, plastic, and soft metals. GDK spindles work with non-ferrous metals and go fast. DX spindles run slower and cut both non-ferrous and ferrous metals.
The table holds your material steady. The frame supports the whole CNC router. A strong frame keeps the router from shaking or bending. This helps you get smooth and accurate cuts. A sturdy frame also stops errors and keeps your workpiece safe. You want a frame that does not vibrate. This helps your cuts stay precise.
The motion system moves the router in three directions. These are X, Y, and Z axes. There are different drive systems like lead screws, ball screws, and rack and pinion. Each system changes how accurate your cuts are. Systems that lower friction and backlash help you get better results. You need to keep the motion system clean and oiled. Taking care of it stops mistakes and keeps your CNC Routing projects working well.
Wood and MDF are popular for CNC Routing. They are easy to cut and shape. Wood is strong and does not break easily. But wood can bend if you do not store it right. MDF is good for making detailed designs and smooth cuts. It is heavy and does not like water. The table below shows what is good and bad about each:
Material | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
MDF | High accuracy, consistent cuts, good for intricate patterns | Sensitive to moisture, creates dust |
Wood | Strong, stable, good for structure | Can warp, needs edge banding |
Tip: Use MDF for signs and panels with lots of detail. Choose wood for furniture or things that need to be strong.
Many plastics work with CNC Routing. Acrylic gives you clear and smooth edges. It is great for displays. Polycarbonate is strong and does not break from heat. But you must watch the temperature so it does not melt. ABS and PETG are simple to cut and shape. They are good for covers, signs, and parts. The table below compares some plastics:
Material | Key Advantages | Machinability | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
Acrylic (PMMA) | Clear, strong | Needs heat control | Displays, optical parts |
Polycarbonate | Tough, heat-resistant | Good, but can melt | Safety shields, lenses |
ABS | Cost-effective, impact-resistant | Easy to machine | Automotive, electronics |
PETG | Flexible, crack-resistant | Easy to cut | Signs, packaging |
Note: Use sharp bits and set the right speed for a smooth finish on plastics.
You can use CNC Routing to cut metals like aluminum. Aluminum looks nice and is good for strong parts. Composites like carbon fiber are light and strong. They need special tools and dust control. Both metals and composites can make your tools wear out fast. You must be careful when working with them. The table below shows some problems you might have:
Material Type | Challenges |
|---|---|
Composite Materials | Tool wear, delamination, heat sensitivity, dust hazards, variable quality |
Traditional Metals | Tool wear, heat, chip formation, surface finish, hardness, cost |
Tip: Always use the right tool and keep your area clean when working with metals and composites.
CNC Routing can shape foam very fast. Foam is good for models, art, and decorations. Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Polyurethane Foam (PU) are used a lot. You can cut, carve, and engrave foam with high detail. This means less waste and more cool shapes. You can also route soapstone, ceramic tile, glass, and mirrors. Each one is different and needs special tools.
Foam: Easy to carve, good for models and art.
Soapstone: Soft, messy, used for art.
Ceramic tile: Works with lasers, good for decoration.
Glass and mirrors: Need diamond tools, used for custom pieces.
Note: Always check what material you have and pick the right bit for the best results.
CNC Routing is used in many industries. It helps make parts for woodworking, sign making, and prototyping. The table below shows how different industries use CNC Routing:
Industry Sector | Applications |
|---|---|
Woodworking | Making furniture and cabinets |
Sign Making | Creating signs for ads and promotions |
Prototyping | Developing products with plastics, wood, and composites |
CNC routers can cut, shape, and engrave materials very accurately. This process is fast and helps avoid mistakes. Factories use CNC routers to make the same part many times. You get results that are always the same.
CNC routers changed how people make furniture and cabinets. You can:
Cut and engrave with great detail.
Use one machine for many jobs.
Save money and use materials better.
Work faster and safer with automatic jobs.
Make sure every piece fits just right.
You can make custom cabinets, tables, and shelves that look nice. CNC Routing lets you try new ideas and make special pieces for homes or businesses.
CNC routers help make signs and art that look cool. Here are some ways people use them:
Make textured surfaces on wood, acrylic, or metal.
Cut letters and shapes for raised designs.
Add LED lights to make signs bright.
Make signs for stores, events, homes, and schools.
You can also use CNC routers for art projects. You can carve patterns, engrave pictures, or build sculptures. CNC Routing helps you turn your ideas into real things.
CNC Routing helps you make prototypes and custom parts fast. You can:
Get exact parts with computer control.
Make many copies that all match.
Create shapes that are hard to make by hand.
Make working prototypes in a few days.
Use strong materials for testing and real use.
Try different designs and see what works best.
You can use metals, plastics, or wood to make parts for machines, models, or inventions. CNC routers help you test ideas and fix problems quickly.
CNC routers can make parts very exact. These machines follow your design closely. The pieces fit together just right. You can create shapes and engravings that are hard to do by hand. Many companies want special products. They buy better machines for better results. New technology helps you make even more detailed work. Multi-axis routers let you cut at different angles. Some routers use five axes. This means you can make very complex parts.
Here is a table that shows how new technology helps:
Evidence Description | Key Points |
|---|---|
Demand for custom products | More investment in advanced machines for higher precision and customization |
New CNC routing technology | Multi-axis routers and better tools open new possibilities |
5-axis CNC routers | Higher precision and detailed work, good return on investment |
Market growth for advanced routers | More demand for 4-axis and 5-axis routers, leading to more innovation |
Tip: CNC routers can reach very tight tolerances. This is hard to do with regular tools.
CNC routers help you finish jobs quickly. These machines work without stopping. You do not need to change things by hand. You can make hard designs much faster than with hand tools. CNC routers help you avoid mistakes. You waste less material.
Here is a table that compares CNC routers and old methods:
Feature | CNC Routing | Traditional Methods |
|---|---|---|
Speed | Much faster because of automation | Slower, needs manual adjustments |
Efficiency | High, with quick turnaround | Takes more time and effort |
Precision | Very high, few errors | More mistakes from human error |
CNC routers can work all day and night.
You can make many copies of the same part. The quality stays the same.
CNC routers work in many areas. These machines help in space research and coal mining. They help in medicine and fashion too. You also see them in aerospace and consumer goods. You can cut wood, plastic, metal, and foam. This lets you make furniture, signs, machine parts, or art.
Space research uses CNC routers for special parts.
The coal industry uses them for equipment.
Medicine uses them for tools and devices.
Fashion designers use them for patterns and accessories.
Aerospace and consumer goods companies use them for high-quality parts.
Note: You can switch materials and projects with the same machine.
You need to plan for the costs of CNC Routing. The price of a CNC router can be high. You pay for the machine, setup, training, and software. However, outsourcing to a capable partner like HRDJM allows you to avoid these high initial costs while still getting professional-grade parts. Here is a table that shows the main costs:
Cost Component | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
Initial Purchase Price | $20,000 |
Installation and Setup | $1,500 |
Training | $1,000 |
Operational Costs (5 Years) | $10,000 ($2,000/year) |
Software | $3,000 |
Hidden Costs | $2,000 |
Total Estimated TCO | $37,500 |
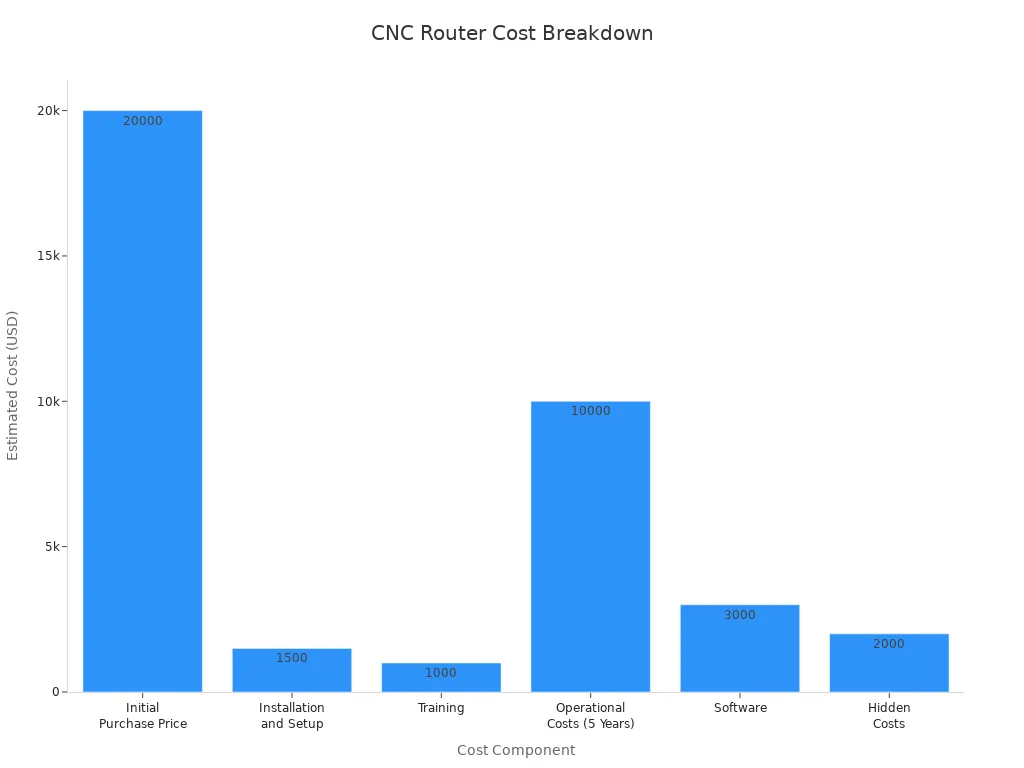
You also need to think about other costs:
Maintenance and repairs can add up each year.
You must buy new cutting tools and supplies often.
Large machines use more electricity.
You pay for wood, metal, or other materials.
Shipping, installation, and workspace upgrades can cost extra.
Software is another cost. Some CAD and CAM programs are free, but others cost thousands of dollars.
You will need time to learn CNC Routing. You must understand the basics, practice with the machine, and learn programming skills. Here are some things that make learning harder:
You need foundational knowledge.
You must get hands-on experience.
You should learn how to program the machine.
You benefit from support networks.
Building a support network helps you improve and solve problems. You can join online forums, local maker spaces, or CNC user groups to share ideas and get advice.
You can make learning easier by:
Watching online tutorials.
Doing practice projects.
Joining support groups.
You must take care of your CNC router to keep it working well. Regular maintenance stops breakdowns and keeps your cuts accurate. Here is a table that shows what you should do and how often:
Maintenance Frequency | Tasks |
|---|---|
Daily | - Clean all debris off machine. |
- Inspect tool holders and internal taper of spindle motor. | |
Weekly | - Check pneumatic oil level and empty water in regulator. |
- Inspect blower filters and grease lead screws and linear guides. | |
Monthly | - Upload machine data and inspect pneumatic connections and electrical enclosures. |
- Clean and grease fourth and fifth axis gear assemblies. | |
Semiannual | - Deep clean lead screw and ball nut assemblies and inspect wiring connections. |
You need to clean the machine every day. You check oil and filters each week. You inspect connections and grease parts each month. Every six months, you do a deep clean and check all wiring. If you skip these steps, your machine can break down or make mistakes.
Benchtop CNC routers are good for small jobs. They fit on a table and do not need much room. Schools and home workshops use them a lot. Makerspaces also like these machines. Benchtop routers cut wood, plastic, and soft metals. You can make signs, models, or tiny parts. The setup is easy for most people. You do not need special skills to use one. You can move the router if you want to change your space.
Tip: A benchtop router is a cheap way to start learning CNC Routing. You can try new ideas and practice with it.
Industrial CNC routers are made for big jobs. Factories and large shops use these machines. They have strong frames and powerful motors. You can cut thick things like aluminum and hardwood. These routers work fast and stay accurate. You can run them all day for lots of parts. Skilled workers need to use and care for them. They have cool features like tool changers and safety systems.
Feature | Hobbyist CNC Routers | Industrial CNC Routers |
|---|---|---|
Size and Construction | Smaller, lighter materials for home use | Larger, strong frames for heavy work |
Precision and Accuracy | Lower precision, fine for simple jobs | Very high precision, good for tiny details |
Spindle Power and Tooling | Low-power spindles, fewer tool choices | High-power spindles, many tool options |
Material Compatibility | Best for wood, plastic, soft metals | Cuts metals, composites, and plastics |
Speed and Throughput | Slower, good for small projects | Fast, great for making many parts |
Automation and Control | Simple controls, less automation | Advanced controls, lots of automation |
Cost Considerations | Cheaper for small shops or hobbyists | Costs more because of better quality |
User-Friendly Interface | Easy for beginners | Needs skilled workers to operate |
Maintenance Requirements | Easy to care for, not often needed | Needs regular care to work well |
Hobby CNC routers are great for crafts and DIY. They cost less and are easy to use. Beginners and small shops like them. Hobby routers work best with wood, acrylic, and soft metals. You can make signs, jewelry, or small furniture. They do not need much space or special power. The controls are simple, so you can start fast.
Hobby routers let you try creative ideas.
You can add new parts as you learn more.
Specialized CNC routers do special jobs. Some are made for cutting foam or engraving glass. Others work with stone or have extra axes for hard shapes. Some use lasers or rotary tools. These routers help you work with unique materials or designs. You get more choices for art, engineering, or science.
Note: If you want to make something different, pick a specialized CNC router that fits your project.
You must protect yourself when you use a CNC router. The machine creates dust, sharp chips, and noise. You need the right gear to stay safe. The table below shows what you should wear and why:
PPE Type | Purpose | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
Respiratory Protection | Protects against fine dust and toxic fumes. | Use N95 masks for dust. Use P100 respirators for more protection. Use organic vapor cartridges for fumes. |
Hand Protection | Prevents cuts and injuries from sharp tools. | Wear cut-resistant gloves during setup. Remove gloves when the machine is running. |
Protective Clothing | Shields skin from debris and prevents snags. | Wear fitted clothing. Avoid loose sleeves. Use aprons or sleeves for extra safety. |
Foot Protection | Protects feet from heavy objects and slips. | Wear steel-toe or composite-toe shoes with slip-resistant soles. |
Tip: Always tie back long hair and remove jewelry before you start.
You must follow safe steps every time you use a CNC router. Start by checking that the work area is clean. Make sure the emergency stop button works. Never leave the machine running alone. Watch the tool and material during the job. If you see sparks or hear strange sounds, stop the machine right away.
Keep your hands away from moving parts.
Use clamps or a vacuum table to hold your material.
Double-check your toolpath before you start.
Stand clear of the spindle when it starts.
Note: You should always read the machine manual before your first use.
You keep your CNC router safe by doing regular checks. Clean dust and chips from the machine after each job. Lubricate moving parts as the manual says. Inspect wires and hoses for damage. Tighten bolts and screws often. Replace worn tools before they break.
Check the emergency stop and safety guards before each use.
Set up your material and tools with the power off.
Store tools and bits in a safe place.
A well-maintained machine works better and keeps you safe.
You should start by thinking about your projects. If you want to make small crafts or signs, a benchtop or hobby router works well. For larger furniture or metal parts, you need a bigger, more powerful machine. Check the size of the work area and the types of materials you want to cut. Look for a router with a sturdy frame and reliable controls. Read reviews and ask other users for advice before you buy.
Tip: Make sure your workspace has enough room for the machine and safe movement around it.
You need more than just the router. Gather these tools before you begin:
Clamps or a vacuum table to hold your material steady.
A set of router bits for wood, plastic, and metal.
Safety gear like goggles, dust masks, and ear protection.
A ruler or caliper for measuring your work.
Lubricant and brushes for cleaning and maintenance.
A good set of tools helps you get better results and keeps your machine in good shape.
You can learn CNC Routing from many places. Start with online tutorials and videos. Many websites offer free guides for beginners. Join forums or maker groups to ask questions and share ideas. Some local community colleges have classes on CNC machines. Books and manuals also help you understand the basics.
Note: Practice with simple designs first. You will build confidence as you go.
You can avoid common mistakes by following these tips:
Tip | Description |
|---|---|
Set Steps Per Unit | Calibrate your router with a ruler to make sure the X, Y, and Z axes move the right amount. |
Verify Soft Limits | Check that the Soft Limits button is on in your control software before you cut. This protects your machine. |
Workpiece Thickness | Adjust the Work Offset for the Z axis if you change the material or tool. This prevents damage and injury. |
Always double-check your setup before you start a job. Careful preparation leads to better results.
You have learned the basics of CNC Routing and its many uses. This tool helps you make precise parts for art, industry, or home projects. You can start small and grow your skills over time. Try simple designs first. Join online groups or take a class to learn more. Explore new ideas and see what you can create! For the highest quality results, consider partnering with experts like HRDJM for your manufacturing needs.
You can cut wood, plastics, foam, and some metals. Each material needs the right bit and speed. Always check your machine’s manual for approved materials.
You do not need to write code. Most CNC routers use software with simple menus. You can draw shapes or import designs. The software creates the toolpaths for you.
You should wear safety gear like goggles and masks. Keep your work area clean. Always check the emergency stop button before starting. Never leave the machine running alone.
Yes, you can sell custom signs, art, or parts. Many small businesses use CNC routers for products. Start with simple projects and build your skills.
A CNC router uses spinning bits to cut or carve. A laser cutter uses a focused light beam. Routers work well for thick materials. Laser cutters make fine, detailed cuts in thin materials.
Tip: Choose the machine that fits your project needs.
Navigation
Navigation
Contact Us
Tel: +86 13417419143
E-mail: [email protected]
Add:
2nd Floor, Building 7, 156 High Tech Industrial Park, Fuyuan 1st Road, Zhancheng Community, Fuhai Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen City, China.